A-LEVEL OCR ChEMISTRY NOTES
Spectroscopy
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
- NMR gives information about the position of 13C or 1H atoms in a molecule
- Nuclei in different chemical environments in the sample molecule will resonate at different frequencies, allowing an NMR spectrum to be produced and interpreted.
- Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is used as a standard to measure an NMR spectrum peak against. The 4 methyl groups are in the same chemical environment and produce an intense signal
- A chemical shift is the scale used in NMR spectroscopy.
- It depends on the molecular environment, hence functional groups have different shifts
- The number of peaks in 13C NMR represents the number of carbon environments in a molecule
- Each peak in a 1H NMR spectrum has an integration trace. This shows the relative number of 1H in each 1H environment
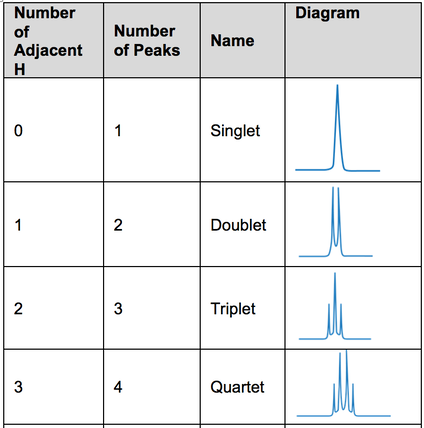
- High resolution 1H also shows spin-spin coupling. This is useful because spin-spin coupling causes splitting patterns which give information about neighbouring hydrogen atoms. The splitting patterns are determined by the N+1 rule
- The N+1 Rule- If there are n hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms adjacent to a 1H environment, then the peak representing that environment will be split into n+1 peaks
- Common solvent used in NMR is CDCl3. ie deuterated solvents.
- In deuterated solvents, any H atoms are replaced with deuterium. They do not affect the spectra