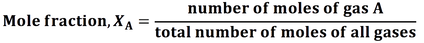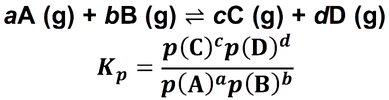A-LEVEL AQA ChEMISTRY NOTES
equilibrium constant kp for homogenous systems
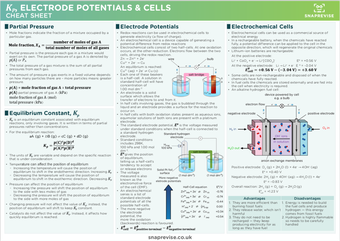
Partial Pressure
- Mole fractions indicate the fraction of a mixture occupied by a particular gas
- Partial pressure is the pressure each gas in a mixture would exert on its own. The partial pressure of a gas A is denoted by or p(A) or PA.
- The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of all partial pressures from each gas.
- The amount of pressure a gas exerts in a fixed volume depends on how many particles there are – more particles means greater pressure.
- p(A) = mole partial pressure of gas A X total pressure
mole of fraction of gas A (mol)
total pressure (kPa)
Equilibrium Constant, Kp
- Kp is an equilibrium constant associated with equilibrium reactions, only involving gases. It is written in terms of partial pressures rather than concentrations.
- For the equilibrium reaction:
- The units of Kp are variable and depend on the specific reaction that is under consideration
- Temperature can affect the position of equilibrium
- Increasing the temperature will cause the position of equilibrium to shift in the endothermic direction. Increasing Kp
- Decreasing the temperature will cause the position of equilibrium to shift in the exothermic direction. Decreasing Kp
- Pressure can affect the position of equilibrium
- Increasing the pressure will shift the position of equilibrium to the side with less moles of gas
- Decreasing the pressure will shift the position of equilibrium to the side with more moles of gas
- Changing pressure will not affect the value of Kp; instead, the position of equilibrium will shift to keep Kp constant.
- Catalysts do not affect the value of Kp. Instead, it affects how quickly equilibrium is reached.