A-LEVEL BIOLOGY AQA NOTES
all cells arise from other cells
Cell Division
- Within multicellular organisms, not all cells retain the ability to divide
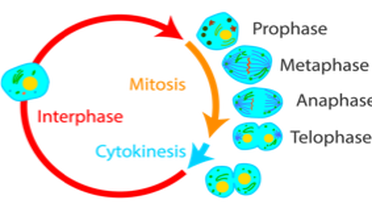
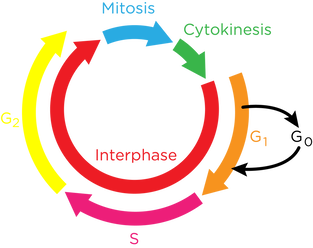
- The eukaryotic cell cycle has three main stages:
- Interphase consists of two growth phases (G1& G2) and a DNA synthesis stage (S). The cell may exit the cell cycle at G0
- Mitosis is the nuclear division
- Cytokinesis is when the cell splits in two, forming two identical daughter cells.
Stage |
Description |
Prophase |
DNA condenses & coils, nuclear envelope breaks down, centrioles move to opposite poles |
Metaphase |
Spindle fibres attach to centromeres & chromosomes line at the equator |
Anaphase |
Centromeres divides, chromatids move to opposite poles |
Telophase |
Chromosomes uncoil, nuclear envelope reforms |
- Cancerous cells have uncontrolled cell division and hence have a modified cell cycle – one that repeats too quickly.
- Treatments for cancer involve disrupting the cell cycle (chemotherapy) by stopping DNA synthesis or by changing the cytoskeleton in mitosis